
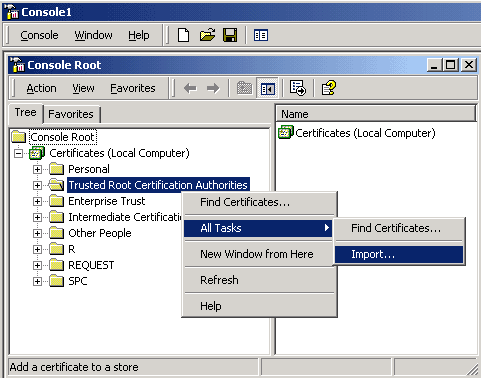
- #Tortoisehg ssl server certificate verify failed install#
- #Tortoisehg ssl server certificate verify failed drivers#
- #Tortoisehg ssl server certificate verify failed driver#
The main determining factor for whether a platform can validate Let’s Encrypt certificates is whether that platform trusts ISRG’s “ISRG Root X1” certificate. Git config -global http.sslCAinfo /etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt Sudo wget -P /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/ Sudo mkdir /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/
#Tortoisehg ssl server certificate verify failed install#
To identify the location of curl-ca-bundle.crt, you could use the command curl-config -caĪlso, see my more recent answer " github: server certificate verification failed": you might have to renistall those certificates: sudo apt-get install -reinstall ca-certificates

openssl s_client -showcerts -servername -connect Findekano adds in the comments: Note: Valeriy Katkov suggests in the comments to add -servername option to the openssl command, otherwise the command isn't showed certificate for in Valeriy's case. | openssl x509 -noout -text | grep "CA Issuers" | head -1 To check the CA (Certificate Authority issuer), type a: echo -n | openssl s_client -showcerts -connect :YourHttpsGilabPort \
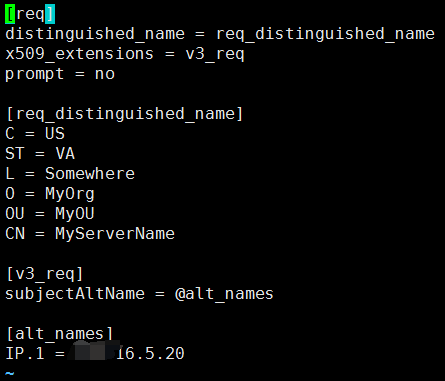
(with ' ' being your GitLab server name, and YourHttpsGitlabPort is the https port, usually 443) To get that certificate (that you would need to add to your curl-ca-bundle.crt file), type a: echo -n | openssl s_client -showcerts -connect :YourHttpsGitlabPort \Ģ>/dev/null | sed -ne '/-BEGIN CERTIFICATE-/,/-END CERTIFICATE-/p'

To check if at least the clone works without checking said certificate, you can set: export GIT_SSL_NO_VERIFY=1īut that would be for testing only, as illustrated in " SSL works with browser, wget, and curl, but fails with git", or in this blog post.Ĭheck your GitLab settings, a in issue 4272. You need to check the web certificate used for your gitLab server, and add it to your /bin/curl-ca-bundle.crt. What you have to do to circumvent the problem on your computer is telling it to trust that certificate - if you don't have any reason to be suspicious about it. This doesn't mean the certificate is suspicious, but it could be self-signed or signed by an institution/company that isn't in the list of your OS's list of CAs. The basic reason is that your computer doesn't trust the certificate authority that signed the certificate used on the Gitlab server. Warning: as noted in gareththered's excellent answer, this adds all certificates, instead of only the Root CAs.īlindly adding all (any) certificate to your trustStore without due diligence is not the best course of action. Sudo bash -c "echo -n | openssl s_client -showcerts -connect $hostname:$port -servername $hostname \Ģ>/dev/null | sed -ne '/-BEGIN CERTIFICATE-/,/-END CERTIFICATE-/p' \ This is the least desirable option as it prevents the connection from being encrypted, meaning that the traffic between your SQL Server and the client can be intercepted and inspected with ease.Trust_cert_file_location=`curl-config -ca` Add Encrypt=false (or Encrypt=no, depending on your programming language) to your connection string.Add TrustServerCertificate=true (or TrustServerCertificate=yes, depending on your programming language) to your connection string, so that the server's certificate is accepted without error and allows secure, encrypted connections, or.crt file and import it into the trusted certificate stores of the users that need to connect to it, or Export the public key portion of the target SQL Server's certificate to a.
#Tortoisehg ssl server certificate verify failed drivers#
Unfortunately, by default, SQL Server instances are installed with self-signed X.509 certificate that are not trusted by any CAs (Certificate Authorities) so most people upgrading to these versions of the drivers are receiving errors similar to yours.
#Tortoisehg ssl server certificate verify failed driver#
ODBC Driver 18 for SQL Server and JDBC Driver 10.2 for SQL Server both default to the Encrypt=yes connection string option with the goal of improving data security for SQL Server users and developers.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
